The difference and application of high-strength bolts and ordinary bolts
High-strength bolts and ordinary bolts are two types of fasteners used in various applications.
Here’s a comparison of their differences and typical applications:
Strength: High-strength bolts are designed to have significantly higher tensile strength and shear strength compared to ordinary bolts. They are made from alloy steel and undergo specialized heat treatment processes to enhance their strength. Ordinary bolts, on the other hand, have lower strength and are typically made from carbon machining steel.
Markings: High-strength bolts often have markings on their heads to indicate their grade or strength class. These markings help identify the bolt’s specifications, such as its tensile strength and material properties. Ordinary bolts usually do not have specific markings related to strength.
Installation: High-strength bolts require precise installation procedures to achieve the desired strength and performance. They are often used in applications where structural integrity and load-bearing capacity are critical. Installation methods for high-strength bolts typically involve using calibrated torque wrenches or hydraulic tensioning equipment to achieve the specified preload. Ordinary bolts are generally easier to install and do not require specialized equipment or torque control.
Applications: High-strength bolts are commonly used in construction, infrastructure projects, bridges, buildings, and other applications where heavy loads or high stress levels are expected. They are essential for joining structural steel members, such as beams, columns, and trusses. Ordinary bolts find use in less demanding applications, including cnc machinery parts furniture assembly, automotive components, non-structural connections, and general-purpose fastening.
Standards: High-strength bolts are often manufactured and specified according to industry standards, such as ASTM A325 and ASTM A490 in the United States. These standards define the material requirements, mechanical properties, dimensions, and installation procedures for high-strength bolts. Ordinary bolts typically follow more general standards, such as ASTM A307, which cover a broader range of applications and lower strength requirements.
What are high strength bolts?
High-Strength Friction Grip Bolt , English literal translation is: high-strength friction pre-tightening bolt, English abbreviation: HSFG. It can be seen that the high-strength bolts mentioned in our Chinese construction are the abbreviations of high-strength friction preload bolts. In daily communication, the words “Friction” and “Grip” are only briefly mentioned, but many engineers and technicians have misunderstood the basic definition of high-strength bolts.
Misunderstanding one:
Bolts with a material grade exceeding 8.8 are “high-strength bolts”?
The core difference between high-strength bolts and ordinary bolts is not the strength of the material used, but the form of force. The essence is whether to apply preload and use static friction to resist shear.
In fact, the high-strength bolts (HSFG BOLT) mentioned in the British standard and the American standard are only 8.8 and 10.9 (BS EN 14399 / ASTM-A325&ASTM-490), while ordinary bolts include 4.6, 5.6, 8.8, 10.9, 12.9, etc. (BS 3692 11 Table 2); it can be seen that the strength of the material is not the key to distinguish high-strength bolts from ordinary bolts.
Correct understanding of “high strength”, where is the strength
According to GB50017, calculate the tensile and shear strength of a single ordinary bolt (Type B) 8.8 grade and high-strength bolt 8.8 grade.
Through calculation, we can see that under the same grade, the design and aluminum cnc service values of tensile strength and shear strength of ordinary bolts are higher than those of high-strength bolts.
So where is the “strong” of high-strength bolts?
In order to answer this question, it is necessary to start with the design working state of the two bolts, study the law of elastic-plastic deformation, and understand the limit state at the time of design failure.
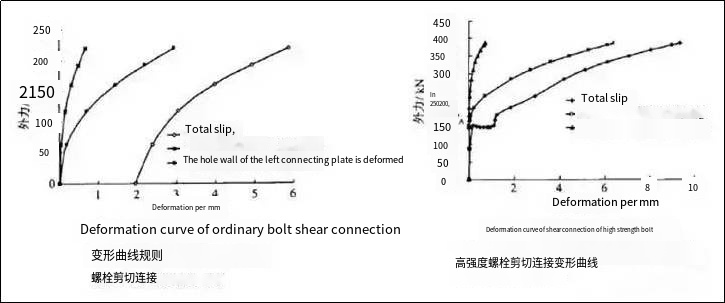
Stress-strain curves of ordinary bolts and high-strength bolts under working conditions
Limit state at design failure
Ordinary bolts: The plastic deformation of the screw itself exceeds the design allowance, and the screw is damaged by shearing.
For ordinary bolt connection, relative slippage will occur between the connecting plates before the shear force begins to bear, and then the bolt rod and the connecting plate contact, elastic-plastic deformation occurs, and the shear force is endured.
High-strength bolts: The static friction between the effective friction surfaces is overcome, and the relative displacement of the two steel plates occurs, which is considered to be damaged in design considerations.
In the high-strength bolt connection, the friction force first bears the shear force. When the load increases to the point where the friction force is not enough to resist the shear force, the static friction force is overcome, and the relative slip of the connecting plate occurs (limit state). However, although it is damaged at this time, the bolt rod is in contact with the connecting plate, and it can still use its own elastic-plastic deformation to withstand the shear force.
Misunderstanding 2:
The bearing capacity of high-strength bolts is higher than that of ordinary bolts. Is it “high strength”?
It can be seen from the calculation of a single bolt that the design strength of high-strength bolts in tension and shear is lower than that of ordinary bolts. Its high-strength essence is: during normal operation, the nodes are not allowed to have any relative slippage, that is, the elastic-plastic deformation is small, and the node stiffness is large.
It can be seen that in the case of a given design node load, a node designed with high-strength bolts may not necessarily save the number of bolts used, but it has small deformation, high stiffness, and high safety reserve. It is suitable for main girders and other locations that require high node stiffness, and conforms to the basic seismic design principle of “strong nodes, weak members”.
The strength of high-strength bolts does not lie in the design value of its own bearing capacity, but in the high stiffness of its design nodes, high safety performance, and strong resistance to damage.
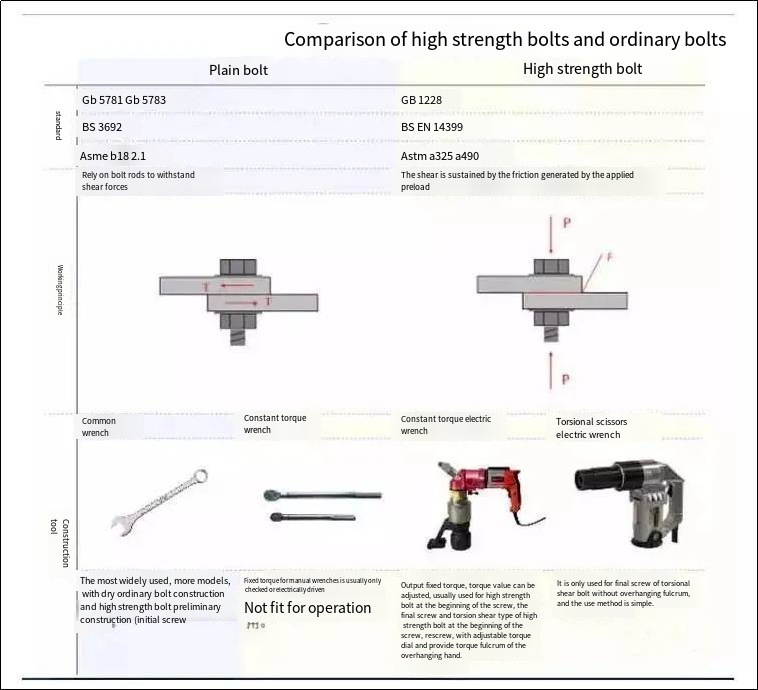
Comparison of high-strength bolts and ordinary bolts
Ordinary bolts and high-strength bolts are very different in construction inspection methods due to their different design principles.
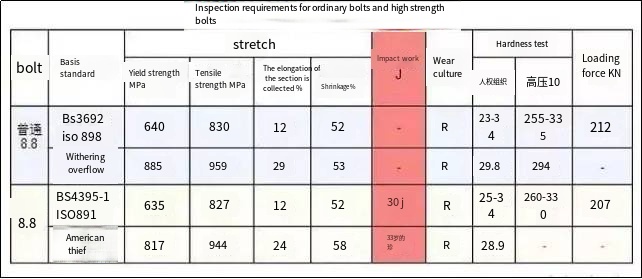
The mechanical performance requirements of ordinary bolts of the same grade are slightly higher than those of high-strength bolts, but high-strength bolts have one more acceptance requirement for impact energy than ordinary bolts.
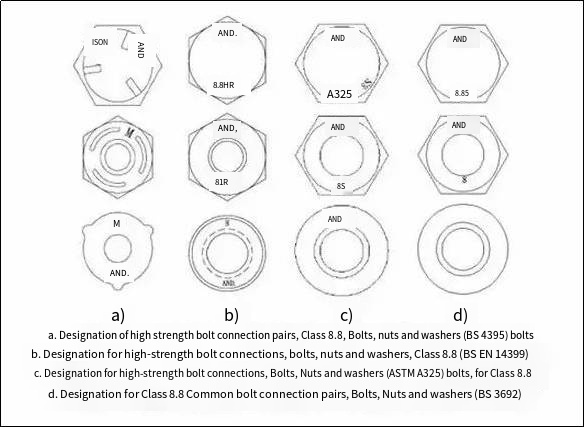
The marking of ordinary bolts and high-strength bolts is the basic method for on-site identification of bolts of the same grade. Since the values calculated for the torque value of high-strength bolts in the British and American standards are not the same, it is also necessary to identify the bolts of the two standards.
High-strength bolts: (M24, L60, grade 8.8)
Ordinary bolts: (M24, L60, grade 8.8)
It can be seen that ordinary bolts are about 70% of the price of high-strength bolts. Combined with the comparison of their acceptance requirements, it can be concluded that the premium part should be to ensure the impact energy (toughness) performance of the material.
Summarize
For a seemingly simple problem, it is not a simple matter to have a deep, comprehensive and correct understanding of its essence. The definition, meaning and profound difference between high-strength bolts and ordinary bolts are the basic premise for us to correctly understand, use high-strength bolts, and carry out construction management.
View:
1) It is indeed stated in some steel structure books that high-strength bolts refer to bolts whose strength exceeds 8.8 grades. For this point of view, first of all, Anglo-American standards do not support it, and there is no definition of “strong” and “weak” for a certain level of strength. Secondly, it does not meet the “high-strength bolts” mentioned in our work.
2) For the convenience of comparison, the stress of complex bolt groups is not considered here.
3) The pressure bearing force of the screw is also considered in the design of the pressure-bearing high-strength bolt, which will be introduced in detail in the following “Comparison of pressure-bearing and friction-type high-strength bolts”.
How much do you know about high-strength bolts?
The full name of high-strength bolts in production is called high-strength bolt connection pair, and it is generally not referred to as high-strength bolts for short.
According to the installation characteristics, it is divided into: large hexagon head bolts and torsional shear bolts. Among them, the torsional shear type is only used in level 10.9.
According to the performance grade of high-strength bolts, it is divided into: 8.8 and 10.9. Among them, there are only large hexagonal high-strength bolts in grade 8.8. In the marking method, the number before the decimal point indicates the tensile strength after heat treatment; the number after the decimal point indicates the yield ratio, that is, the ratio of the measured value of yield strength to the measured value of ultimate tensile strength. . Grade 8.8 means that the tensile strength of the bolt shaft is not less than 800MPa, and the yield ratio is 0.8; Grade 10.9 means that the tensile strength of the bolt shaft is not less than 1000MPa, and the yield ratio is 0.9.
The diameters of high-strength bolts in structural design generally include M16/M20/M22/M24/M27/M30, but M22/M27 is the second choice series, and M16/M20/M24/M30 is the main choice under normal circumstances.
In terms of shear design, high-strength bolts are divided into: high-strength bolt pressure-bearing type and high-strength bolt friction type according to design requirements.
The bearing capacity of the friction type depends on the anti-slip coefficient of the force transmission friction surface and the number of friction surfaces. The friction coefficient of red rust after sandblasting (shot) is the highest, but it is greatly affected by the construction level in terms of actual operation. Many supervision units They all raised whether the standard can be lowered to ensure the quality of the project.
The load-bearing capacity of the pressure-bearing type depends on the minimum value of the shear capacity of the bolt and the pressure-bearing capacity of the bolt. In the case of only one connecting surface, the shear bearing capacity of the M16 friction type is 21.6-45.0 kN, while the shear capacity of the M16 pressure-bearing type is 39.2-48.6 kN, and the performance is better than that of the friction type.
In terms of installation, the pressure-bearing type process is simpler, and the connection surface only needs to be cleaned of oil and floating rust. The tensile bearing capacity along the shaft direction is very interesting in the steel structure code. The design value of the friction type is equal to 0.8 times the pre-tension force, and the design value of the pressure type is equal to the effective area of the screw multiplied by the design value of the tensile strength of the material. It seems that There is a big difference, in fact, the two values are basically the same.
When bearing shear force and tensile force in the direction of the rod axis at the same time, the friction type requires that the ratio of the shear force borne by the bolt to the shear capacity plus the sum of the stress ratio of the axial force borne by the screw to the tensile capacity is less than 1.0, and the pressure type requires It is the sum of the square of the ratio of the shear force to the shear capacity of the bolt plus the square of the ratio of the axial force to the tensile capacity of the screw is less than 1.0, that is to say, under the same load combination, the same diameter of the bearing The safety reserve of the design of high-strength bolts is higher than that of friction-type high-strength bolts.
Considering that under the repeated action of strong earthquakes, the connection friction surface may fail, and the shear capacity at this time still depends on the shear capacity of the bolt and the pressure capacity of the plate. Therefore, the seismic code stipulates the ultimate shear capacity of high-strength bolts Bearing capacity calculation formula.
Although the pressure-bearing type has an advantage in the design value, because it belongs to the shear-compression failure type, the bolt holes are pore-type bolt holes similar to ordinary bolts, and the deformation under load is much larger than that of the friction type, so the high-strength bolts bear pressure The type is mainly used for non-seismic component connections, non-dynamic load component connections, and non-repetitive component connections.
The normal service limit states of these two types are also different:
Friction type connection refers to the relative slippage of the connection friction surface under the basic combination of loads;
The pressure-bearing connection refers to the relative slippage between the connecting parts under the load standard combination;
Common bolt
1. Ordinary bolts are divided into three types: A, B, and C. The first two are refined bolts, less used. Generally speaking, ordinary bolts refer to C-level ordinary bolts.
2. In some temporary connections and connections that need to be disassembled, C-level ordinary bolts are commonly used. Common bolts commonly used in building structures are M16, M20, M24. Some rough bolts in the mechanical industry may have a relatively large diameter and are used for special purposes.
High strength bolts
3. The material of high-strength bolts is different from ordinary bolts. High-strength bolts are generally used for permanent connections. Commonly used are M16~M30. The performance of oversized high-strength bolts is unstable and should be used with caution.
4. The bolt connection of the main components of the building structure is generally connected by high-strength bolts.
5. The high-strength bolts delivered by the factory are not classified into pressure-bearing or friction-type.
6. Are they friction-type high-strength bolts or pressure-bearing high-strength bolts? In fact, there is a difference in the design calculation method:
1) For friction-type high-strength bolts, the sliding between the plates is regarded as the limit state of the bearing capacity.
2) For pressure-bearing high-strength bolts, the sliding between the plates is regarded as the limit state of normal use, and the connection failure is regarded as the limit state of bearing capacity.
7. Friction-type high-strength bolts cannot give full play to the potential of the bolts. In practical applications, friction-type high-strength bolts should be used for very important structures or structures subjected to dynamic loads, especially when the load causes reverse stress. At this time, the unused bolt potential can be used as a safety reserve. In other places, pressure-bearing high-strength bolts should be used to reduce the cost.
The difference between ordinary bolts and high-strength bolts
8. Ordinary bolts can be reused, but high-strength bolts cannot be reused.
9. High-strength bolts are generally made of high-strength steel (No. 45 steel (8.8s), 20MmTiB (10.9S), which are prestressed bolts. The friction type uses a torque wrench to apply the specified prestress, and the pressure type unscrews the plum blossom head. Ordinary Bolts are generally made of ordinary steel (Q235) and only need to be tightened.
10. Ordinary bolts are generally grade 4.4, grade 4.8, grade 5.6 and grade 8.8. High-strength bolts are generally grade 8.8 and grade 10.9, of which grade 10.9 is the majority.
11. The screw holes of ordinary bolts are not necessarily larger than those of high-strength bolts. In fact, ordinary bolts have relatively small screw holes.
12. The screw holes of A and B grades of ordinary bolts are generally only 0.3~0.5mm larger than the bolts. Class C screw holes are generally 1.0~1.5mm larger than bolts.
13. Friction-type high-strength bolts transmit loads by friction, so the difference between the screw rod and the screw hole can reach 1.5-2.0mm.
14. The force transmission characteristics of pressure-bearing high-strength bolts are to ensure that under normal use, the shear force does not exceed the friction force, which is the same as that of friction-type high-strength bolts. When the load increases again, relative slippage will occur between the connecting plates, and the connection relies on the shear resistance of the screw and the pressure of the hole wall to transmit the force, which is the same as that of ordinary bolts, so the difference between the screw and the screw hole is slightly smaller, 1.0-1.5mm.
Anebon adheres on the tenet “Honest, industrious, enterprising, innovative” to acquire new solutions continuously. Anebon regards prospects, success as its personal success. Let Anebon build prosperous future hand in hand for brass machined parts and Complex titanium cnc parts / stamping accessories. Anebon now has comprehensive goods supply as well as selling price is our advantage. Welcome to inquire about Anebon’s products.
Trending Products China CNC Machinging Part and Precision Part, really should any of these items be of interest to you, please let us know. Anebon will be pleased to give you a quotation upon receipt of one’s detailed specifications. Anebon have our personal specialist R&D enginners to meet any of the requriements. Anebon look forward to receiving your enquires soon and hope to have the chance to work together with you inside the future. Welcome to take a look at Anebon organization.
Post time: Jun-01-2023