A summary of eight processing methods of thread you must know when machining.
.The English word corresponding to Screw is Screw. The meaning of this word has changed a lot in recent hundreds of years. At least in 1725, it means "mating".
The application of the thread principle can be traced back to the spiral water-lifting tool created by the Greek scholar Archimedes in 220 BC.
In the 4th century AD, the Mediterranean countries began to apply the principle of bolts and nuts to the presses used in winemaking. At that time, the external thread was wound with a rope to a cylindrical bar and then carved according to this mark, while the internal thread was often formed by hammering the external thread with a softer material.
Around 1500, in the sketch of the thread processing device drawn by the Italian Leonardo da Vinci, there was an idea of using the female Screw and the exchange gear to process threads with different pitches. Since then, the method of mechanically cutting threads has developed in the European watchmaking industry.
In 1760, the British brothers J. Wyatt and W. Wyatt obtained a patent for cutting wood screws with a particular device. In 1778, the British J. Ramsden once manufactured a thread-cutting device driven by a worm gear pair, which can process long threads with high precision. In 1797, the Englishman H. Maudsley used the female Screw and exchange gear to turn metal threads of different pitches on his improved lathe, which laid the primary method of turning threads.
In the 1820s, Maudsley produced the first taps and dies for threading.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the development of the automobile industry further promoted the standardization of threads and the development of various precise and efficient thread-processing methods. Various automatic opening die heads and automatic shrinking taps were invented one after another, and thread milling began to be applied.
In the early 1930s, thread grinding appeared.
Although the thread rolling technology was patented in the early 19th century, due to the difficulty of mold manufacturing, the development was prolonged until the Second World War (1942-1945) due to the need for arms production and the development of thread grinding technology. The precision problem of mold manufacturing has developed rapidly. CNC turning part
Threads are mainly divided into connecting threads and transmission threads.
The central processing methods for connecting threads are tapping, threading, threading, thread rolling, thread rolling, etc.
The central processing methods for transmission threads are rough and fine turning---grinding, whirl milling---coarse and fine turning, etc.
The first category is thread-cutting
It generally refers to machining workpiece threads with forming or abrasive tools, mainly including turning, milling, tapping and thread grinding, grinding, and whirling cutting. When turning, milling, and grinding threads, the drive chain of the machine tool ensures that the turning tool, milling cutter, or grinding wheel moves precisely and evenly one lead along the axis of the workpiece for each revolution of the workpiece. When tapping or threading, the tool (tap or die) and the workpiece rotate relative to each other, and the previously formed thread groove guides the tool (or workpiece) to move axially.
1. Thread turning
Thread turning on a lathe can be done with a forming turning tool or a thread comb. Turning threads with a forming turning tool is a standard method for single-piece and small batch production of threaded workpieces due to the simple tool structure; turning threads with a thread combing tool has high production efficiency, but the tool structure is complex, only suitable for medium and large batch production. They are turning short thread workpieces with fine pitch. The pitch accuracy of ordinary lathes for turning trapezoidal threads can generally only reach 8 to 9 grades (JB2886-81, the same below); machining threads on specialized thread lathes can significantly improve productivity or accuracy.

2. Thread milling
I was milling with a disc or comb cutter on a thread mill.
Disc milling cutters are mainly used for milling trapezoidal external threads on workpieces such as screws and worms comb-shaped milling cutter is used for milling internal and external common threads and tapered threads. Since it is milled with a multi-blade milling cutter and the length of its working part is greater than the length of the thread, the workpiece only needs to be rotated 1.25 to 1.5 turns to be processed and done with high productivity. The pitch accuracy of thread milling can generally reach 8 to 9 grades, and the surface roughness is R5 to 0.63 microns. This method is suitable for mass-producing threaded workpieces of general precision or roughing before grinding.
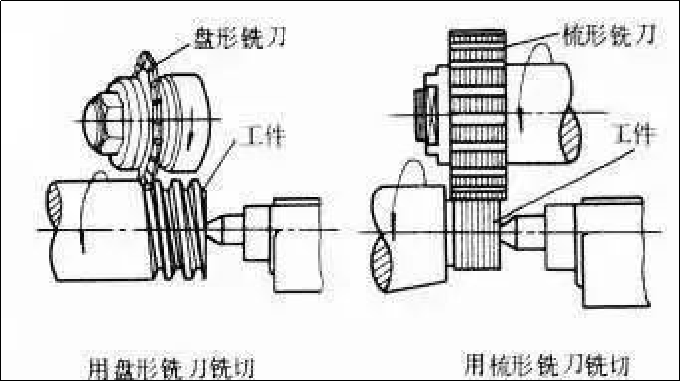
Thread milling cutter for machining internal threads
3. Thread grinding
It is mainly used to process precision threads of hardened workpieces on thread-grinding machines. The shape of the cross-section of the grinding wheel can be divided into two types: single-line grinding wheel and multi-line grinding wheel. The pitch accuracy achieved by single-line grinding wheel grinding is 5 to 6 grades, and the surface roughness is R1.25 to 0.08 microns, which is more convenient for grinding wheel dressing. This method is suitable for grinding precision screws, thread gauges, worms, small batches of threaded workpieces, and relief grinding precision hobs. Multi-line grinding wheel grinding is divided into longitudinal and plunge grinding methods. In the longitudinal grinding method, the width of the grinding wheel is smaller than the length of the thread to be ground, and the grinding wheel moves longitudinally once or several times to grind the thread to the final size. The width of the grinding wheel of the plunge grinding method is larger than the length of the thread to be ground. The grinding wheel is cut radially into the surface of the workpiece, and the workpiece can be ground well after about 1.25 revolutions. The productivity is high, but the precision is slightly lower, and the grinding wheel dressing is more complicated. Plunge grinding is suitable for relief grinding large batches of taps and for grinding specific threads for fastening. aluminum extrusion parts
4. Thread grinding
The nut-type or screw-type thread grinder is made of soft materials such as cast iron, and the parts where the thread has a pitch error on the workpiece are subjected to forward and reverse rotation grinding to improve pitch accuracy. Hardened internal threads are usually ground to eliminate deformation and improve accuracy.
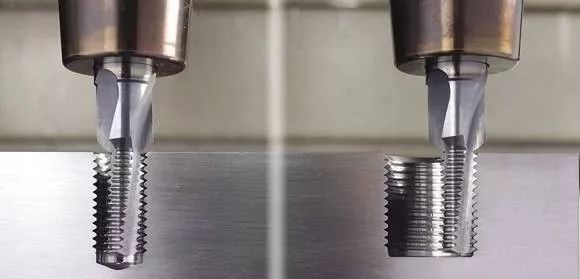
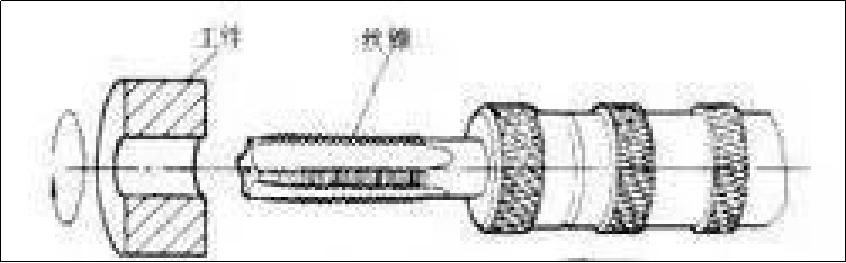
5. Tapping and threading
Tapping
It is to screw the tap into the pre-drilled bottom hole on the workpiece with a specific torque to process the internal thread.
Thread
Cut the external thread on the bar (or pipe) workpiece with a die. The machining accuracy of tapping or threading depends on the accuracy of the tap or die. aluminum parts
Although there are many ways to process internal and external threads, small-diameter internal threads can only be processed by taps. Tapping and threading can be performed by hand, as well as by lathes, drill presses, tapping machines, and threading machines.
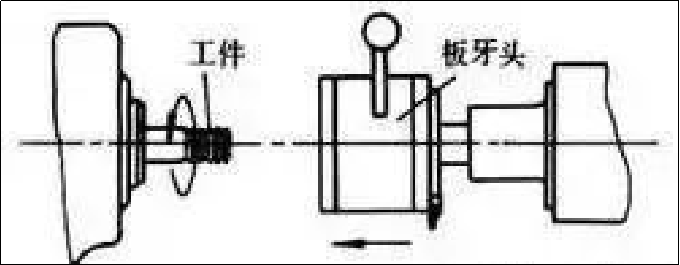
The second category: Thread rolling
The processing method of plastically deforming the workpiece with a forming rolling die to obtain a thread. Thread rolling is generally performed on a Thread rolling machine or an automatic lathe with an automatic opening and closing Thread rolling head, an external thread for mass production of standard fasteners, and other threaded couplings. The outer diameter of the rolled Thread isThreadally not more than 25 mm, the length is not more than 100 mm, the thread accuracy can reach level 2 (GB197-63), and the diameter of the blank used is roughly equal to the pitch diameter of the processed Thread. RThread generally cannot process internal threads, but for workpieces with softer materials, a grooveless extrusion tap can be used to cold-extrude internal threads (the maximum diameter can reach about 30 mm). The working principle is similar to that of tapping. The torque required for cold extrusion of internal threads is about 1 times larger than that of tapping, and the machining accuracy and surface quality are slightly higher than those of tapping.
Advantages of Thread rolling:
①The surface roughness is smaller than that of turning, milling, and grinding;
②The surface of the Thread afThreadlling can improve the strength and hardness due to cold work hardening;
③The material utilization rate is high;
④The productivity is doubled compared to cutting, and it is easy to realize automation;
⑤ The life of the rolling die is very long. However, rolling Thread reThread that the hardness of the workpiece material does not exceed HRC40; the dimensional accuracy of the blank is high; the precision and hardness of the rolling die are also high, and it is difficult to manufacture the die; it is not suitable for rolling threads with asymmetric tooth shape.
According to the different rolling dies, Thread can be divided into two types: Thread rolling and Threadthreadd
6. Thread rolling
Two thread rolling plates with threaded tooth shapes are arranged opposite each other with a 1/2 pitch; the static plate is fixed, and the moving plate moves in a reciprocating linear motion parallel to the static plate. When the workpiece is sent between the two plates, the moving plate moves forward and rubs the workpiece to plastically deform the surface to form a thread (Figure 6 [Screwing]).
7. Thread rolling
There are three types of radial Thread roThread, tangential Thread roThread, and rolling head thread rolling.
①Radial Threathreadad 2 (or 3) thread rolling wheels with thread profiles are installed on mutually parallel shafts; the workpiece is placed on the support between the two wheels, and the two wheels rotate in the same direction and at the same speed (Figure 7). [Radial Thread rolling]), one of the rounds, also performs radial feed motion. The thread rolling wheel rotates the workpiece, and the surface is radially extruded to form threads. For some lead screws that do not require high precision, a similar method can also be used for roll forming.
②Tangential Thread roThread Also known as planetary Thread roThread, the rolling tool consists of a rotating central thread rolling wheel and three fixed arc-shaped thread plates (Fig. 8 [Tangential Thread rolling]). The workpiece can be continuously fed during Thread thread, so the productivity is higher than that of Thread roThreadand radial Thread thread
③ Thread rethreaded: It is carried out on an automatic lathe and is generally used to process short threads on the workpiece. There are 3 to 4 thread rolling wheels evenly distributed on the outer periphery of the workpiece in the rolling head (Fig. 9 [Thread rethreaded rolling]). During thread rolling, the workpiece rotates, and the rolling head feeds axially to roll the workpiece out of the Thread.
Thread threading
The processing of ordinary threads generally uses machining centers or tapping equipment and tools; sometimes, manual tapping is also possible. However, in some exceptional cases, the above method is not easy to obtain good processing results, such as the need to machine threads after heat treatment of parts due to negligence or due to material constraints, such as the need to tap directly on carbide workpieces. At this time, it is necessary to consider the pEDM processing method.
Compared with the machining method, the EDM process is in the same order: the bottom hole needs to be drilled first, and the diameter of the bottom hole should be determined according to the working conditions. The electrode needs to be machined into a thread shape, and the electrode needs to be able to rotate during the machining process.
Anebon Metal Products Limited can provide CNC Machining、Die Casting、Sheet Metal Fabrication service, please feel free to contact us.
Tel: +86-769-89802722 E-mail: info@anebon.com URL: www.anebon.com
Post time: Apr-15-2022
