How much do you know about machined threads?
In the realm of machining, “threads” typically refer to the helical ridges and valleys on the surface of a cylindrical part, which enable it to be connected with another part or be used to transmit motion or power. The definitions and standards for machined threads are often specific to the industry and application in question.In the United States, machined threads are commonly defined by standards set by organizations such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). These standards specify thread profiles, pitch, tolerance classes, and other parameters for various types of threads.
One of the most well-known standards for machined threads is the Unified Thread Standard (UTS), which is used for inch-based threads. The UTS defines various thread series, such as Unified Coarse (UNC) and Unified Fine (UNF), and provides detailed specifications for thread dimensions, tolerances, and designations.For metric threads, the ISO metric screw thread standard (ISO 68-1) is widely used. This standard covers metric thread profiles, thread pitch, tolerance classes, and other related specifications.It’s important to refer to the specific standards and specifications relevant to the industry and application you are working with to guarantee proper design and manufacturing of machined threads.
Every day, technicians working with machinery encounter threaded components. Regardless of their specifications—be it metric or imperial, straight or tapered, sealed or unsealed, internal or external, with a 55-degree or 60-degree profile—these components often become damaged and are rendered unusable over time. It is essential to thoroughly inspect them from start to finish. Today, the Anebon team will compile a summary in the hope that it will benefit everyone.
1. Common symbols
NPT is a general-use American standard tapered pipe thread with a 60° profile angle.
PT thread is an imperial tapered thread with a 55° thread angle, commonly used for sealing. British pipe threads feature fine threads. Due to the large thread depth of coarse threads, it significantly reduces the strength of the outer diameter pipe being cut.
PF thread is a parallel thread for pipes.
G is a 55-degree non-threaded sealing pipe thread, belonging to the Whitworth thread family. The marking G represents a cylindrical thread, with G being the general term for pipe thread (Guan), and the differentiation between 55 degrees and 60 degrees is functional.
ZG is commonly known as a pipe cone, which means the thread is processed from a conical surface. General water pipe joints are made in this manner. The old national standard is marked Rc.Pitch is used to express metric threads, while the number of threads per inch is used for American and British threads. This is their primary distinction. Metric threads have a 60-degree equilateral profile, British threads have a 55-degree isosceles profile, and American threads have a 60-degree profile.
Metric threads use metric units, while American and British threads use imperial units.
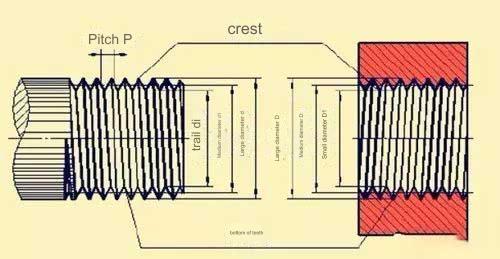
Pipe threads are primarily used for connecting pipes. The internal and external threads are closely matched, and there are two types: straight pipes and tapered pipes. The nominal diameter refers to the diameter of the connected pipe. Clearly, the major diameter of the thread is larger than the nominal diameter.
The application scope covers cnc machined parts, cnc turning parts and cnc milling parts.
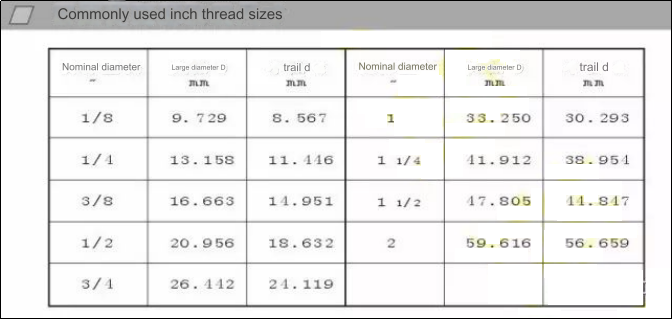
1/4, 1/2, and 1/8 represent the nominal diameters of inch threads in inches.
2. Different country standards
1. Unified inch system thread
This type of thread is commonly utilized in countries that use the inch system and is categorized into three series: coarse thread series UNC, fine thread series UNF, extra fine thread series UNFF, and fixed pitch series UN.
Marking method: Thread diameter—number of threads per inch series code—accuracy grade.
For example: Coarse thread series 3/8—16UNC—2A; Fine thread series 3/8—24UNF—2A; Extra fine thread series 3/8—32UNFF—2A;
Fixed pitch series 3/8—20UN—2A.The first digit 3/8 denotes the outer diameter of the thread in inches. To convert to the metric unit mm, multiply by 25.4, which equals 9.525mm; the second and third digits 16, 24, 32, and 20 represent the number of teeth per inch (the number of teeth on a length of 25.4mm); the text codes after the third digit, UNC, UNF, UNFF, UN, are the series codes, and the last two digits, 2A, indicate the accuracy level.
Conversion of 2.55° cylindrical pipe thread
The 55° cylindrical pipe thread originated from the inch series but is extensively utilized in both metric and inch countries. It is employed for connecting pipe joints, transporting liquids and gases, and installing wires. However, different countries have different codes, so it is necessary to convert foreign codes into Chinese codes using the table (comparison table) provided. The 55° cylindrical pipe thread codes of various countries are now presented in the table below.
| Country |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conversion of 3.55° tapered pipe thread
55° tapered pipe thread means that the thread profile angle is 55° and the thread has a taper of 1:16. This series of threads are widely used in the world, and its code names vary from country to country.
|
Country
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PT、R | |
|
|
|
4.Conversion of 60° tapered pipe thread
60° tapered pipe thread refers to a pipe thread with a profile angle of 60° and a thread taper of 1:16. This series of threads are used in my country’s machine tool industry and the United States and the former Soviet Union. Its code name, China used to specify it as K, later specified it as Z, and now it is changed to NPT. See the thread code comparison table below.
|
Country
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| USA | NPT | |
|
|
|
5.55° Trapezoidal Thread Conversion
Trapezoidal thread refers to a metric trapezoidal thread with a profile angle of 30°. This series of threads are relatively uniform at home and abroad, and their codes are also quite consistent. The thread codes are shown in the table below.
|
Country
|
|
|
|
|
| ISO | Tr |
|
|
|
| German | Tr |
3. Thread classification
According to different uses of threads, they can be divided into:
1. International Metric Thread System
The thread adopted by my country’s national standard CNS. The top of the tooth is flat and easy to turn, while the bottom of the tooth is arc-shaped to increase the strength of the thread. The thread angle is 60 degrees, and the specification is expressed in M. Metric threads can be divided into two types: coarse thread and fine thread. The representation is as M8x1.25. (M: code, 8: nominal diameter, 1.25: pitch).
2. American Standard Thread
The top and root of the thread are both flat and have better strength. The thread angle is also 60 degrees, and the specifications are expressed in threads per inch. This kind of thread can be divided into three levels: coarse thread (NC); fine thread (NF); extra fine thread (NEF). The representation is such as 1/2-10NC. (1/2: outer diameter; 10: number of teeth per inch; NC code).
3. Unified standard thread (UnifiedThread)
Jointly formulated by the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada, it is the commonly used British thread.
The thread angle is also 60 degrees, and the specifications are expressed in threads per inch. This kind of thread can be divided into coarse thread (UNC); fine thread (UNF); extra fine thread (UNEF). The representation is such as 1/2-10UNC. (1/2: outer diameter; 10: number of teeth per inch; UNC code).
4.V-shaped thread (Sharp VThread)
The top and roots are both pointed, weak in strength, and not commonly used. The thread angle is 60 degrees.
5. Whitworth Thread
This thread type is specified by the British National Standard. It features a thread angle of 55 degrees and is symbolized by “W”. Primarily designed for rolling manufacturing processes, it is often represented as W1/2-10 (1/2: outer diameter; 10: number of teeth per inch; W code).
6. Round Thread (KnuckleThread)
This standard thread type, established by the German DIN, is highly suitable for connecting light bulbs and rubber tubes. It is denoted by the symbol “Rd”.
7. Pipe Thread (PipeThread)
Designed to prevent leaks, these threads are commonly used for connecting gas or liquid pipes. With a thread angle of 55 degrees, they can be further divided into straight pipe threads, known as “P.S., N.P.S.”, and tapered pipe threads, known as “N.P.T.”. The taper is 1:16, equivalent to 3/4 inch per foot.
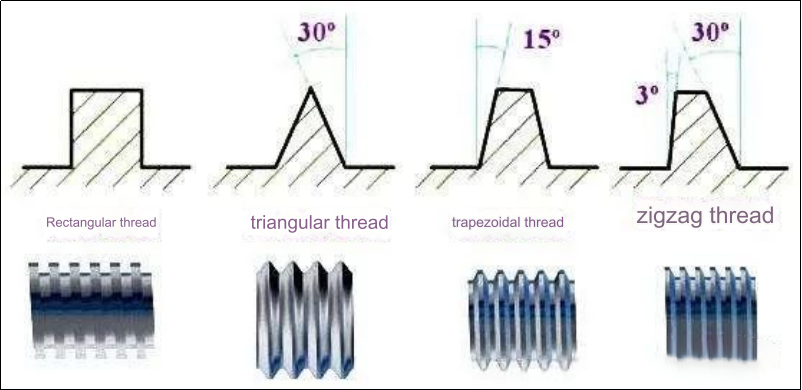
8. Square Thread
Featuring high transmission efficiency, second only to the ball thread, this thread type is often utilized for vise screws and crane threads. However, its limitation lies in the inability to be adjusted with a nut after wear.
9. Trapezoidal Thread
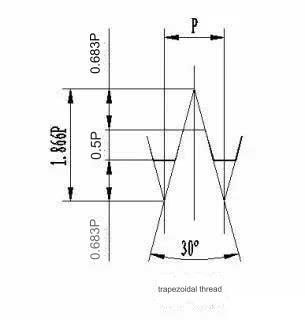
Also referred to as Acme thread, this type offers slightly lower transmission efficiency than the square thread. However, it has the advantage of being adjustable with a nut after wear. In the metric system, the thread angle is 30 degrees, while in the imperial system, it is 29 degrees. Typically used for the lead screws of lathes, it is represented by the symbol “Tr”.
10.Zigzag thread (ButtressThread)
Also called rhombic thread, it is only suitable for one-way transmission. Such as screw jacks, pressurizers, etc. The symbol is “Bu”.
11. Ball thread
It is the thread with the best transmission efficiency. It is difficult to manufacture and extremely costly. It is used in precision machinery. Such as the lead screw of CNC machine tools and prototype machined parts.
Representation of inch bolts
LH 2N 5/8 × 3 – 13UNC-2A
(1) LH is left thread (RH is right thread and can be omitted).
(2) 2N double thread.
(3) 5/8 inch thread, outer diameter 5/8”.
(4) 3 bolt length 3”.
(5) 13 threads have 13 threads per inch.
(6) UNC unified standard thread coarse thread.
(7) Level 2 fit, external thread (3: tight fit; 2: medium fit; 1: loose fit) A: External thread (can be omitted), B: Internal thread.
Imperial thread
The size of imperial threads is usually expressed by the number of threads per inch of length on the thread, referred to as the “number of threads per inch”, which is exactly equal to the reciprocal of the thread pitch. For example, a thread with 8 threads per inch has a pitch of 1/8 inch.
Anebon pursuit and company purpose is always to “Always satisfy our consumer requirements”. Anebon keep on to acquire and style and design remarkable high-quality products for each our outdated and new customers and reach a win-win prospect for Anebon’s consumers as well as us for Original Factory Profile extrusions aluminum, cnc turned part, cnc milling nylon. We sincerely welcome friends to barter business enterprise and start cooperation with us. Anebon hope to hitch hands with close friends in different industries to produce a brilliant long run.
China Manufacturer for China High Precision and Metal Stainless Steel Foundry, Anebon is seeking the chances to meet all the friends from both at home and abroad for the win-win cooperation. Anebon sincerely hope to have long-term cooperation with all of you on the bases of mutual benefit and common development.
If you would like to learn more or have parts to estimate pricing, please feel free to contact info@anebon.com
Post time: Jan-03-2024