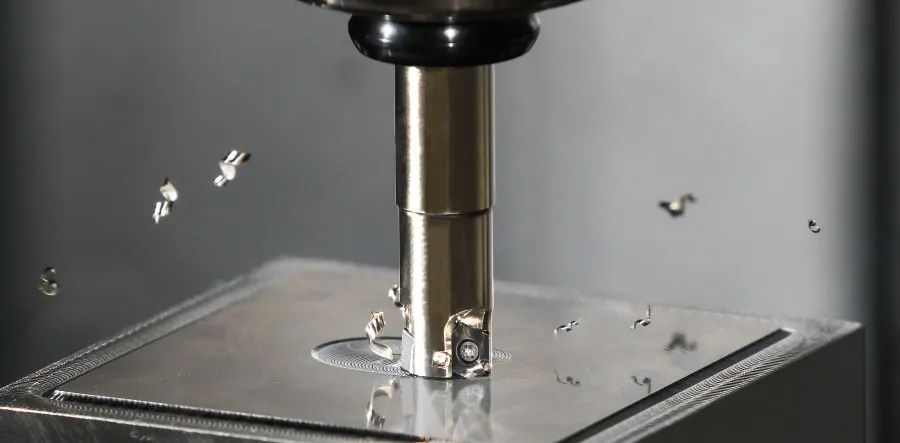
What is a CNC tool?
The combination of advanced processing equipment and high-performance CNC cutting tools can give full play to its due performance and achieve good economic benefits. With the rapid development of cutting tool materials, various new cutting tool materials have greatly improved their physical, mechanical properties and cutting performance, and their application range has also continued to expand.
The structural composition of CNC tools?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) tools are machine tools that are operated by programmed commands encoded on a storage medium, such as a computer. These tools use a computer-controlled system to perform precision machining operations, such as cutting, drilling, milling, and shaping. The tools are used in manufacturing processes, particularly in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and metalworking.
CNC tools include a range of machines, such as CNC milling machines, CNC lathe process, CNC routers, CNC plasma cutters, and CNC laser cutters. These tools operate by moving a cutting tool or workpiece in three or more axes using computer numerical control.
CNC tools are known for their precision, accuracy, and repeatability, which makes them ideal for manufacturing complex parts and components with tight tolerances. They are also capable of producing high-quality products at a faster rate than traditional manual machines, which helps to increase productivity and efficiency in manufacturing.
What basic properties should CNC tool materials have?
1. Hardness: CNC tool materials should be hard enough to resist wear and tear during the machining process.
2. Toughness: CNC tool materials should be tough enough to withstand impact and shock loads.
3. Heat resistance: CNC tool materials should be able to withstand high temperatures generated during the machining process without losing their strength or durability.
4. Wear resistance: CNC tool materials should be resistant to abrasive wear caused by contact with the workpiece.
5. Chemical stability: CNC tool materials should be chemically stable to avoid corrosion and other forms of chemical damage.
6. Machinability: CNC tool materials should be easy to machine and shape into the desired form.
7. Cost-effectiveness: CNC tool materials should be affordable and cost-effective, considering their performance and longevity.
Types, properties, characteristics and applications of cutting tool materials
Each type of material has its unique properties, characteristics, and applications. Here are some common cutting tool materials, along with their properties and applications:
1. High-Speed Steel (HSS):
HSS is a commonly used cutting tool material, made from a combination of steel, tungsten, molybdenum, and other elements. It is known for its high hardness, wear resistance, and toughness, making it suitable for machining a wide range of materials, including steels, aluminum alloys, and plastics.
2. Carbide:
Carbide is a composite material made from a mixture of tungsten carbide particles and a metallic binder, such as cobalt. It is known for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and heat resistance, making it ideal for machining tough materials, such as stainless steel, cast iron, and high-temperature alloys.
3. Ceramic:
Ceramic cutting tools are made from a variety of ceramic materials, such as aluminum oxide, silicon nitride, and zirconia. They are known for their high hardness, wear resistance, and chemical stability, making them suitable for machining hard and abrasive materials, such as ceramics, composites, and superalloys.
4. Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN):
CBN is a synthetic material made from cubic boron nitride crystals. It is known for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and heat resistance, making it suitable for machining hardened steels and other materials that are difficult to machine using other cutting tool materials.
5. Diamond:
Diamond cutting tools are made from natural or synthetic diamonds. They are known for their exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and heat resistance, making them suitable for machining non-ferrous metals, composites, and other hard and abrasive materials.
There is also a special kind of tool called a coated tool.
Generally, the above materials are used as coatings, and they are widely used in CNC machine tools.
A coated tool is a tool with a thin layer of material applied to its surface to improve its performance and extend its lifespan. The coating material is chosen based on the tool’s intended use, and common coating materials include titanium nitride (TiN), titanium carboni (TiCN), and diamond-like carbon (DLC).
Coatings can improve a tool’s performance in various ways, such as reducing friction and wear, increasing hardness and toughness, and improving resistance to corrosion and chemical damage. For example, a TiN-coated drill bit can last up to three times longer than an uncoated One, and a TiCN-coated end mill can cut through harder materials with less wear.
Coated tools are commonly used in industries such as manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. They can be used for cutting, drilling, milling, grinding, and other machining operations.
Selection principles of CNC tool materials
The selection of CNC tool materials is an important consideration when designing and manufacturing precision turning parts. The selection of a tool material is based on a number of factors, including the type of material being machined, the machining operation, and the desired finish.
Here are some of the selection principles of CNC tool materials:
1. Hardness: The tool material must be hard enough to withstand the forces and temperatures generated during machining. Hardness is typically measured on the Rockwell C scale or the Vickers scale.
2. Toughness: The tool material must also be tough enough to resist fracture and chipping. Toughness is usually measured by impact strength or fracture toughness.
3. Wear resistance: The tool material should have good wear resistance to maintain its cutting edge and avoid tool failure. The wear resistance of a material is often measured by the volume of material that is removed from the tool during a certain amount of machining.
4. Thermal conductivity: The tool material should have good thermal conductivity to dissipate heat generated during machining. This helps to avoid tool failure and to maintain dimensional accuracy.
5. Chemical stability: The tool material should be chemically stable to avoid chemical reactions with the workpiece material.
6. Cost: The cost of the tool material is also an important consideration, especially for high-volume production runs.
Common materials used for CNC tooling include carbide, high-speed steel, ceramic, and diamond. The selection of a tool material depends on the specific machining operation and the desired finish, as well as the materials being machined and the available equipment.
1)The cutting tool material matches the mechanical properties of the machined object
Matching the cutting tool material to the mechanical properties of the machined object is an important consideration in CNC machining. The mechanical properties of the machined object include its hardness, toughness, and ductility, among others. Choosing a cutting tool material that matches or complements the mechanical properties of the machined object can improve machining performance and efficiency, reduce tool wear, and improve the quality of the finished part.
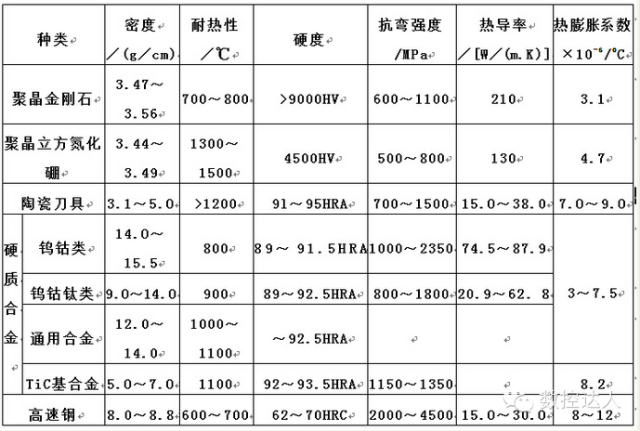
① The order of tool material hardness is: diamond tool>cubic boron nitride tool>ceramic tool>tungsten carbide>high-speed steel.
② The order of bending strength of tool materials is: high-speed steel > cemented carbide > ceramic tools > diamond and cubic boron nitride tools.
③ The order of toughness of tool materials is: high-speed steel > cemented carbide > cubic boron nitride, diamond and ceramic tools.
For example, if the machined object is made of a hard and brittle material like hardened steel or cast iron, a cutting tool made of a hard and wear-resistant material like carbide or ceramic may be the best choice. These materials can withstand the high cutting forces and temperatures generated during machining and maintain their sharp cutting edges for longer periods of time.
On the other hand, if the machined object is made of a softer and more ductile material like aluminum or copper, a cutting tool made of a tougher material like high-speed steel may be more appropriate. High-speed steel can better absorb shock and vibration during machining, reducing the risk of tool breakage and improving tool life.
2)Matching of cutting tool material to the physical properties of the machined object
Matching the cutting tool material to the physical properties of the machined object is also an important consideration in CNC machining. The physical properties of the machined object include its thermal conductivity, coefficient of thermal expansion, and surface finish requirements, among others. Choosing a cutting tool material that matches or complements the physical properties of the machined object can improve machining performance, reduce tool wear, and improve the quality of the finished part.
① Heat-resistant temperature of various tool materials: 700-8000C for diamond tools, 13000-15000C for PCBN tools, 1100-12000C for ceramic tools, 900-11000C for TiC(N)-based cemented carbide, and 900-11000C for WC-based ultrafine grains Cemented carbide is 800~9000C, HSS is 600~7000C.
②The order of thermal conductivity of various tool materials: PCD>PCBN>WC-based cemented carbide>TiC(N)-based cemented carbide>HSS>Si3N4-based ceramics>A1203-based ceramics.
③ The order of thermal expansion coefficient of various tool materials is: HSS>WC-based cemented carbide>TiC(N)>A1203-based ceramics>PCBN>Si3N4-based ceramics>PCD.
④The order of thermal shock resistance of various tool materials is: HSS>WC-based cemented carbide>Si3N4-based ceramics>PCBN>PCD>TiC(N)-based cemented carbide>A1203-based ceramics.
For example, if the machined object has a high thermal conductivity, like copper or aluminum, a cutting tool with a high thermal conductivity and low coefficient of thermal expansion may be the best choice. This allows the tool to dissipate heat efficiently during machining and reduces the risk of thermal damage to both the tool and the machined object.
Similarly, if the machined object has strict surface finish requirements, a cutting tool with a high wear resistance and low coefficient of friction may be the best choice. This can help to achieve the desired surface finish without excessive tool wear or damage to the machined object.
3)Matching the cutting tool material to the chemical properties of the machined object
Matching the cutting tool material to the chemical properties of the machined object is also an important consideration in CNC machining. The chemical properties of the machined object include its reactivity, corrosion resistance, and chemical composition, among others. Choosing a cutting tool material that matches or complements the chemical properties of the machined object can improve machining performance, reduce tool wear, and improve the quality of the finished part.
For example, if the machined object is made of a reactive or corrosive material like titanium or stainless steel, a cutting tool made of a corrosion-resistant material like diamond or PCD (polycrystalline diamond) may be the best choice. These materials can withstand the corrosive or reactive environment and maintain their sharp cutting edges for longer periods of time.
Similarly, if the machined object has a complex chemical composition, a cutting tool made of a material that is chemically stable and inert, like diamond or cubic boron nitride (CBN), may be the best choice. These materials can avoid chemical reactions with the workpiece material and maintain their cutting performance over time.
① The anti-bonding temperature of various tool materials (with steel) is: PCBN>ceramic>hard alloy>HSS.
② The oxidation resistance temperature of various tool materials is as follows: ceramic>PCBN>tungsten carbide>diamond>HSS.
③The diffusion strength of the tool materials (for steel) is: diamond>Si3N4-based ceramics>PCBN>A1203-based ceramics. Diffusion intensity (for titanium) is: A1203-based ceramics>PCBN>SiC>Si3N4>diamond.
4)Reasonable selection of CNC cutting tool materials
The selection of CNC cutting tool materials depends on various factors such as the workpiece material, the machining operation, and the tool geometry. However, some general guidelines for selecting cutting tool materials for CNC machining include:
1. Material properties of the workpiece: Consider the mechanical, physical, and chemical properties of the workpiece material when selecting the cutting tool material. Match the cutting tool material to the workpiece material to achieve efficient and high-quality machining.
2. Machining operation: Consider the type of machining operation being performed, such as turning, milling, drilling, or grinding. Different machining operations require different cutting tool geometries and materials.
3. Tool geometry: Consider the cutting tool geometry when selecting the tool material. Choose a material that can maintain a sharp cutting edge and withstand the cutting forces generated during the machining operation.
4. Tool wear: Consider the tool wear rate when selecting the cutting tool material. Choose a material that can withstand the cutting forces and maintain its sharp cutting edge for as long as possible to minimize tool changes and improve machining efficiency.
5. Cost: Consider the cost of the cutting tool material when selecting the tool. Choose a material that provides the best balance of cutting performance and cost.
Some common cutting tool materials used in CNC machining include high-speed steel, carbide, ceramic, diamond, and CBN. Each material has its advantages and disadvantages, and the selection of the tool material should be based on a thorough understanding of the machining operation and workpiece material.
Anebon’s eternal pursuits are the attitude of “regard the market, regard the custom, regard the science” and the theory of “quality the basic, trust the first and management the advanced” for Hot sale Factory OEM Service High Precision CNC Machining parts for automation industrial, Anebon quote for your inquiry. For more information, please get in touch with us, Anebon will reply you ASAP!
Hot sale Factory China 5 axis cnc machining parts, CNC turned parts and milling copper part. Welcome to visit our company, factory and our showroom where displays various hair merchandise that will meet your expectation. Meanwhile, it is convenient to visit Anebon’s website, and Anebon sales staff will try their best to deliver you the best service. Please contact Anebon if you have to have more information. Aim of Anebon is to help customers realize their goals. Anebon have been making great efforts to achieve this win-win situation.
Post time: Mar-08-2023