What are eccentric parts?
Eccentric parts are mechanical components that have an off-center axis of rotation or an irregular shape that causes them to rotate in a non-uniform manner. These parts are often used in machines and mechanical systems where precise movements and control are required.
One common example of an eccentric part is an eccentric cam, which is a circular disc with a protrusion on its surface that causes it to move in a non-uniform way as it rotates. Eccentric parts can also refer to any component that is intentionally designed to rotate off-center, such as a flywheel with an uneven distribution of mass.
Eccentric parts are often used in applications such as engines, pumps, and conveyor systems where precise movements and control are required. They can help to reduce vibration, improve performance, and increase the lifespan of the machinery.
Introduction
In the transmission mechanism, eccentric parts such as eccentric workpieces or crankshafts are generally used to complete the function of mutual conversion between rotary motion and reciprocating motion, so eccentric parts are widely used in mechanical transmission. The level of eccentric parts processing technology (especially large eccentric workpieces) can reflect the machining technology capabilities of an enterprise.
Eccentric workpieces play an important role in actual production and life. In mechanical transmission, turning rotary motion into linear motion or converting linear motion into rotary motion is generally completed by eccentric workpieces or crankshafts. For example, the lubricating oil pump in the spindle box is driven by the eccentric shaft, and the rotary motion of the crankshaft of the automobile and tractor is driven by the reciprocating linear motion of the piston.
Professional terms/nouns
1) Eccentric workpiece
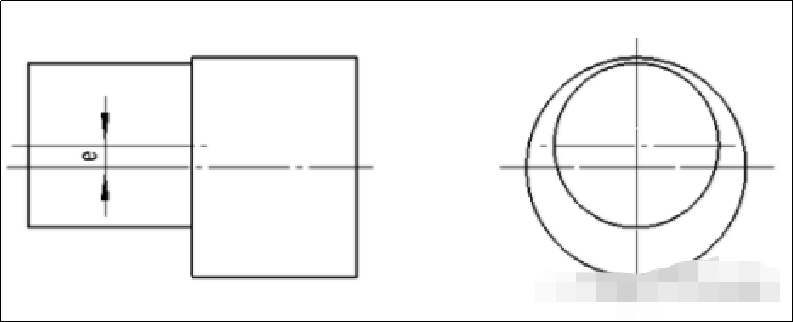
The workpiece whose axes of the outer circle and the outer circle or the outer circle and the inner hole are parallel but not coincident becomes an eccentric workpiece.
2) Eccentric shaft
The workpiece whose axes of the outer circle and the outer circle are parallel and not coincident is called an eccentric shaft.
3) Eccentric sleeve
The workpiece whose axes of the outer circle and the inner hole are parallel but not coincident is called an eccentric sleeve.
4) Eccentricity
In an eccentric workpiece, the distance between the axis of the eccentric part and the axis of the reference part is called the eccentricity.
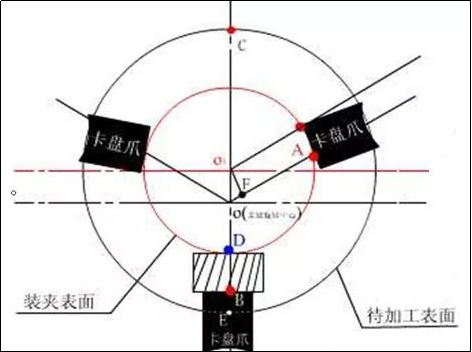
The three-jaw self-centering chuck is suitable for eccentric workpieces that do not require high turning precision, small eccentric distance, and short length. When turning, the eccentricity of the workpiece is guaranteed by the thickness of the gasket placed on a jaw.
Although the traditional processing methods of eccentric CNC machining parts and the improved three-jaw turning method can complete the task of processing eccentric workpiece parts, the defects of difficult processing, low efficiency, interchangeability and precision are difficult to guarantee. Modern high-efficiency and high-precision machining concepts cannot tolerate of.
The Principle, Method and Points to Note of Eccentricity of Three-jaw Chuck
The principle of the eccentricity of the three-jaw chuck: adjust the rotation center of the workpiece surface to be processed to be concentric with the axis of the machine tool spindle. Adjust the geometric centroid of the clamping part to the distance from the spindle axis equal to the eccentricity.
Gasket thickness calculation (initial, final) l Gasket thickness calculation formula: x=1.5e+k where:
e—workpiece eccentricity, mm;
k——Correction value (obtained after the test run, that is, k≈1.5△e), mm;
△e—the error between the measured eccentricity and the required eccentricity after the test run (ie △e=e-e measurement), mm;
e measurement – the measured eccentricity, mm;
Example 1
Turning the workpiece with the eccentricity of 3mm, if the thickness of the gasket is turned with a trial selection, the measured eccentricity is 3.12mm, and the correct value of the thickness of the gasket is found. l Solution: The thickness of the trial gasket is:
X=1.5e=1.5×3mm=4.5mm
△e=(3-3.12)mm=-0.12mm
K=1.5△e=1.5×(-0.12)mm=-0.18mm
According to the formula: x=1.5e+k=(4.5-0.18) mm=4.32mm
The correct value for the gasket thickness is 4.32mm.
Example 2
A gasket with a thickness of 10mm is used to turn the eccentric workpiece on a jaw pad of the three-jaw self-centering chuck. After turning, the eccentricity of the workpiece is measured to be 0.65mm smaller than the design requirement. Find the correct value for the gasket thickness.
Known eccentricity error △e=0.65mm
Approximate gasket thickness: X test=1.5e=10mm
K=1.5△e=1.5×0.65mm=0.975mm
According to the formula: x=1.5e+k=(10+0.975)mm=10.975mm
The correct value for gasket thickness is 10.975mm.
Disadvantages of eccentric three-jaw turning
Eccentric three-jaw turning, also known as eccentric chucking, is a turning processwhere a workpiece is held in a chuck that has three jaws that are not centered withthe chuck’s axis. Instead, one of the jaws is set off-center, creating an eccentricrotation of the workpiece.
While eccentric three-jaw turning has some advantages, such as the ability to turnirregularly shaped parts and reducing the need for specialized tooling, it also hassome disadvantages, including:
1. lnaccurate centering: Because the workpiece is held off-center, it can be difficult toaccurately center it for precise machining operations. This can result in parts thatare out of tolerance or have uneven surfaces.
2. Reduced holding power: The off-center jaw has less gripping power than the2other two jaws, which can result in a less secure hold on the workpiece. This cancause the workpiece to shift or slip during machining, leading to inaccurate cutsand potentially dangerous situations.
3. Increased tool wear: Because the workpiece is not centered, the cutting tool mayexperience uneven wear, which can result in shorter tool life and increased costsfor tool replacement.
4. Limited range of parts: Eccentric chucking is generally best suited for small to4.medium-sized parts, and cnc turning part with a regular shape. lt may not be suitable forlarger or more complex parts, as the off-center jaw may not provide enoughsupport.
5. Longer setup time: Setting up the chuck for eccentric turning can be more time-consuming than setting up a standard chuck, as it requires careful positioning ofthe off-center jaw to achieve the desired eccentricity.
In CNC Lathe, the eccentric parts are typically created by machining the part on alathe using a special eccentric chuck or a fixture that holds the part off-center.
The following are the general steps to create eccentric parts in CNC lathe:
1. Choose a suitable eccentric chuck or fixture that fits the workpiece and allows for
the desired eccentricity.
2. Set up the lathe with the chuck or fixture and mount the workpiece securely.
3. Use the lathe’s software to set the offset for the desired eccentricity.
4. Program the CNC machine to cut the part according to the desired design,making sure to account for the offset in the cutting path.
5. Run a test program to ensure that the part is being cut correctly and that theeccentricity is within the desired tolerance.
6. Make any necessary adjustments to the cutting program or setup to achieve the desired results.
7. Continue cutting the part until it is completed, making sure to periodically checkthe eccentricity and make any necessary adjustments.
Overall, creating eccentric parts in CNC lathe requires careful planning and preciseexecution to ensure that the final product meets the desired specifications.
The above articles are exclusively provided by the Anebon team, infringement must be investigated
Anebon is a manufacturing company based in Shenzhen, China that specializes in providing customized CNC machining services. The company offers a wide range of manufacturing services, including CNC milling, turning, drilling, and grinding, as well as surface treatment and assembly services.
Anebon has experience working with a variety of materials, including aluminum, brass, stainless steel, titanium, and plastics, and can produce parts with complex geometries and tight tolerances. The company uses advanced equipment, such as 3-axis and 5-axis CNC machines, as well as inspection equipment, to ensure high-quality products.
In addition to CNC machining services, Anebon also offers prototyping services, allowing customers to quickly test and refine their designs before moving to mass production. The company prides itself on its commitment to customer service and quality, and works closely with customers to ensure their specific needs and requirements are met.
Post time: Feb-27-2023